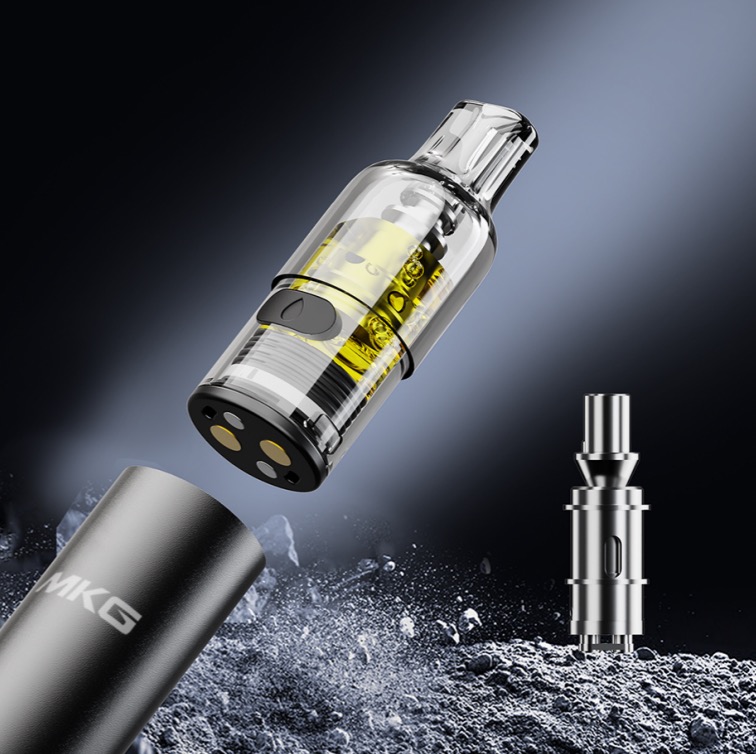
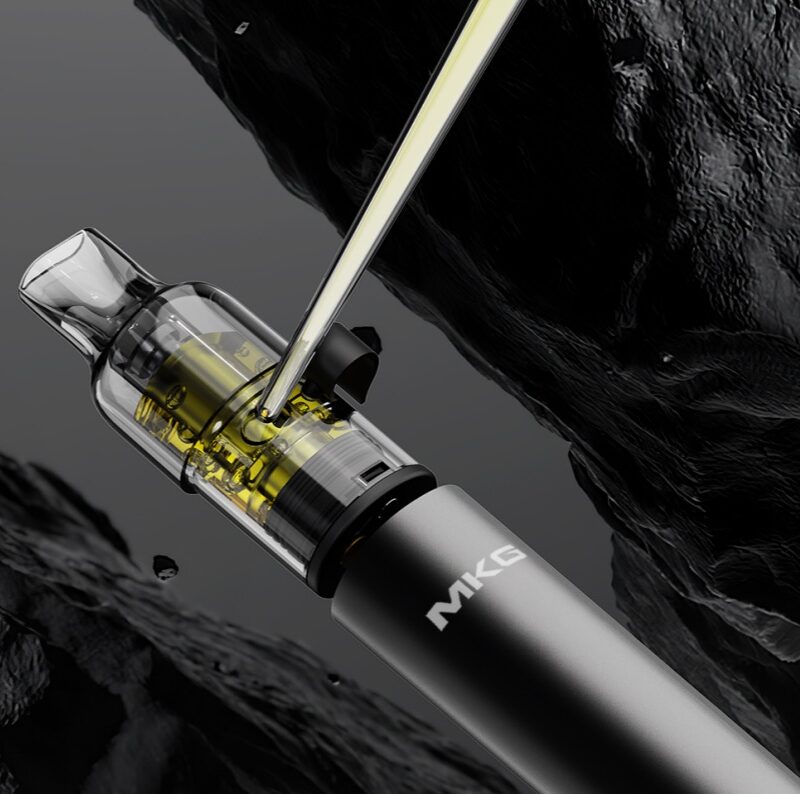
The mesh core is one of the common types of atomization cores in e-cigarettes. The preparation processes for the heating mesh include etching, stamping, weaving, etc. Among them, the etching process is a common method. This article will take an in-depth look at its related metal etching processes.
This article describes metal etching and types, key points and precautions of the etching process.
What is metal etching?
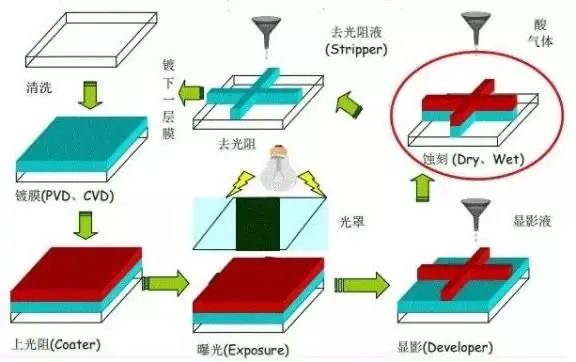
Metal etching, also known as photochemical etching, refers to the removal of the protective film in the metal etching area after exposure, plate making, development, and contact with chemical solutions during the metal etching process to achieve dissolving corrosion, formation of bumps, or hollowing out, technology The route can be divided into wet etching and dry etching.
It was first used to make printed concave and convex plates such as copper plates and zinc plates. It is widely used to reduce the weight of instrument panels or process thin workpieces such as nameplates.
Through continuous improvements in technology and process equipment, etching technology has now been used in aviation, machinery, chemical industry, and semiconductor manufacturing processes to process electronic thin parts and precision metal etching products.
Types of etching techniques
1. Wet etching:
Wet etching is to immerse the workpiece in a suitable chemical solution or spray the chemical solution onto the workpiece for quenching. The atoms on the surface of the film are removed through the chemical reaction between the solution and the object to be etched, thereby achieving the purpose of etching.
When wet etching is performed, the reactants in the solution first diffuse through the stagnant boundary layer, and then reach the wafer surface, where chemical reactions occur and various products are produced. The products of the etching chemical reaction are liquid or gas phase products, which then diffuse through the boundary layer and dissolve into the main solution.
Wet etching will not only etch in the vertical direction, but also have a horizontal etching effect.

2. Dry etching:
Dry etching is usually a type of plasma etching or chemical etching. Due to the different etching effects, the physical atoms of the ions in the plasma, the chemical reactions of active free radicals, and the surface atoms of the device (wafer), or a combination of both, include the following:
Physical etching: sputter etching, ion beam etching
Chemical Etching: Plasma Etching
Physical and chemical composite etching: reactive ion etching (RIE)

Dry etching is an anisotropic etching with good directionality but poorer selectivity than wet etching. In plasma etching, plasma is a partially dissociated gas in which gas molecules are dissociated into electrons, ions and other highly chemically active species.
The biggest advantage of dry etching is “anisotropic etching”. However, (radical) dry etching is less selective than wet etching. This is because the etching mechanism of dry etching is physical interaction; therefore, the impact of ions can not only remove the etching film, but also remove the photoresist mask.