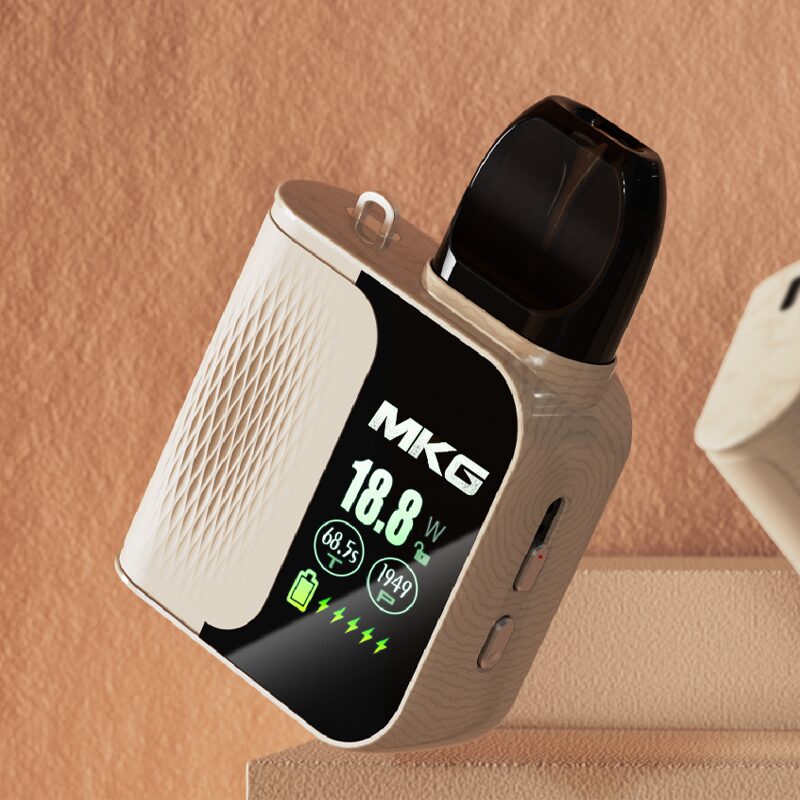
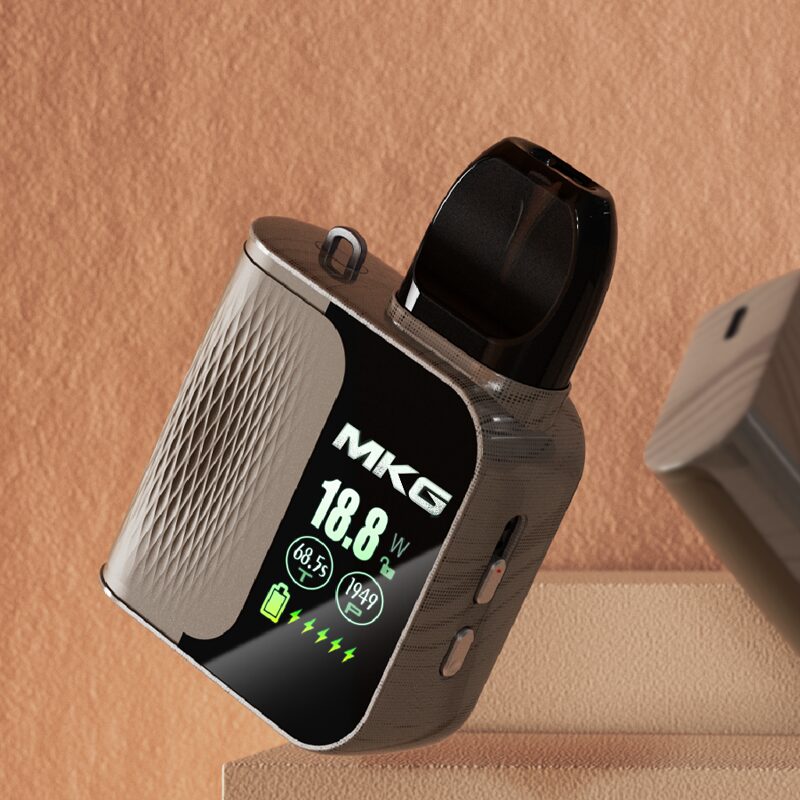
There are three ways of heat transfer: heat conduction, heat radiation and heat convection. According to the principle of heat transfer, heating methods can be divided into: contact heating and non-contact heating, such as resistance heating, electromagnetic induction heating, microwave heating, far-infrared radiation heating, chemical reaction heating, phase change heat pipe convection heating, laser heating, radio wave Heating etc.
1. Resistance heating
The Joule effect of electric current is used to convert electrical energy into thermal energy to heat objects. Usually divided into direct resistance heating and indirect resistance heating.
Direct resistance heating: Since heat is generated from the heated object itself, it is internal heating and has high thermal efficiency, such as electronic cigarette cotton core heating wire, cylindrical heating wire, thick film ceramic heating resistor, HNB heating sheet, etc.
Indirect resistance heating: The heating element needs to be made of special materials. The heating element generates heat energy and transfers it to the heated object through radiation, convection and conduction, such as HNB threaded heating rods.
2. Electromagnetic induction heating
The DC power passes through the converter to form an AC power supply. After the current passes through the eddy current heating element wrapped around the heating cavity (or buried in the cavity wall), an electromagnetic field is formed in the heating cavity. The electromagnetic field acts on the magnetic induction heater (buried in the HNB The bullet hits) and forms eddy currents, generating heat through eddy current losses and hysteresis losses.
3. Microwave heating
Microwaves mainly have three characteristics: penetration, reflection, and absorption. Polar molecules in dielectric materials can be heated by microwaves. Microwave heating will cause the spin movement of polar molecules, and then the microwave energy is converted into thermal energy of the material to be heated, causing the temperature of the material to rise rapidly, resulting in a series of physical and chemical processes such as thermalization.
4. Laser heating
In terms of laser heating and atomization, electrical energy is converted into light energy and emitted to the cone end of the heat collector, so that the smoke liquid at the gathering point is atomized to generate aerosol, and the temperature of the heater can be adjusted to adjust the atomization rate.
5. Far infrared heating
Radiation is a non-contact heat transfer method. It is a phenomenon in which an object emits radiant energy outward due to the thermal movement of microscopic particles inside the object. After the carbon fiber is energized, it radiates energy outwards in the form of thermal radiation, and the radiation rate is high. By controlling the temperature of the carbon fiber heating element so that its radiation wavelength is close to the absorption wavelength of the e-liquid solvent, atomization can be achieved to the maximum extent. Radiant heating can also be used in the HNB field.
6. Phase change heat pipe heating
The manufacturing method of phase change heat pipes generally adopts vacuum filling or liquid filling first and then vacuuming, which uses it to change the physical phase at a specific temperature (phase change temperature) to cause the process of endothermic and exothermic (liquid-gas) -liquid). This principle can be used to transport heat, separate the heat generation source and the final release end, and increase the possibility of more innovative designs of new tobacco appliances.
7. Heating for chemical reactions
Carbon combustion (applicable to HNB): Traditional carbon heat source fuel low-temperature cigarettes are a method that mainly uses convective heat transfer. It was later improved to transfer carbonaceous fuel to the atomization zone through a heat conduction structure.
The physical and chemical reaction is to bring the two isolated substances into contact to form a chemical reaction that releases heat, and the released heat is used to atomize the atomization chamber.