Driven by the continuous expansion of the global e-cigarette market, e-cigarette vaporization technology has entered a stage of rapid development. Brands are emerging one after another. As the core component of e-cigarettes, atomizer cores have experienced sudden technological advancements, and the atomization taste experience is constantly innovating and surpassing. It is the continuous updating and iteration of atomizer cores that promotes the rapid development of e-cigarettes.
Up to now, the atomizing core technology has experienced a total of 6 generations of development, as follows:
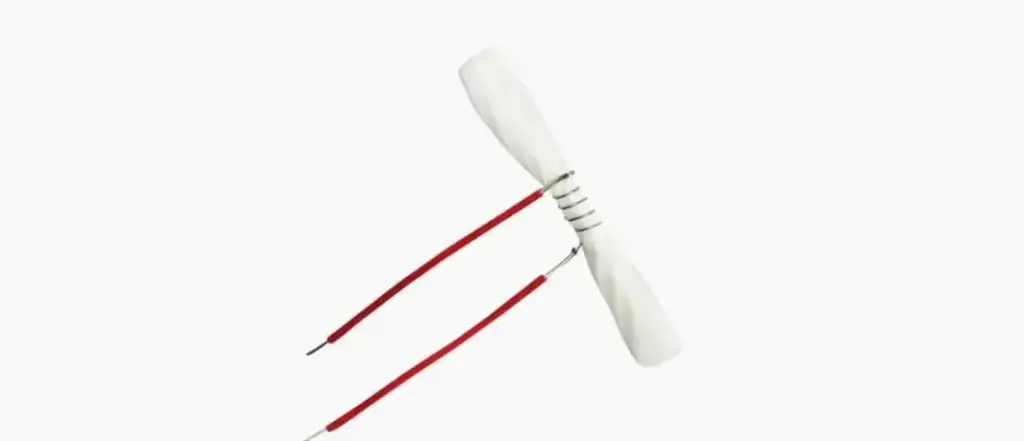
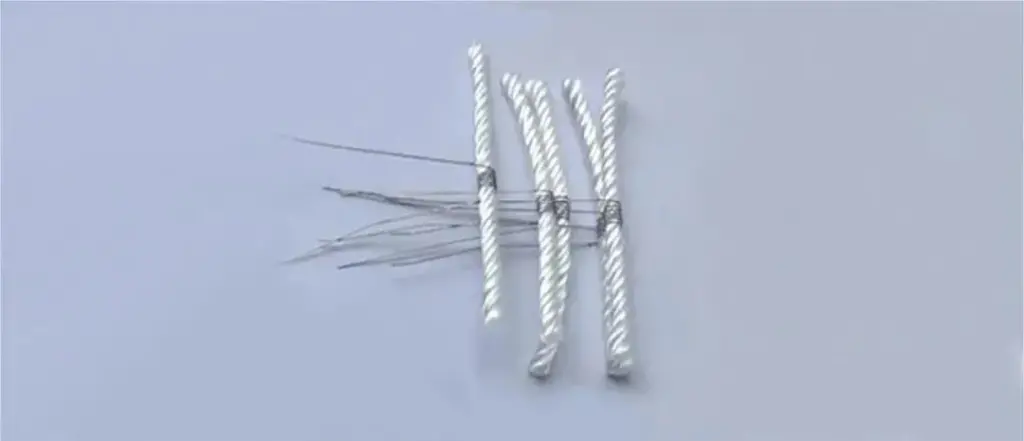
The first generation atomizing core: fiberglass rope

In 2003, Han Li invented the first nicotine-based e-cigarette, which has since brought e-cigarettes into the public eye. Han Li’s invention is known as the first person to invent e-cigarettes in the history of e-cigarette development in China. This period belongs to the birth period of electronic cigarettes and is also the initial pioneering era of electronic cigarette atomizer cores, that is, the first generation of atomizer cores: glass fiber ropes wrapped with heating wires.
The fiberglass rope at that time was resistant to high temperatures, had a high oil absorption rate, and conducted oil very quickly, achieving an atomization effect. However, the fiberglass rope was in contact with the human body and would irritate the skin, causing symptoms such as allergies, redness, swelling, and itching.
Second generation atomizer core: cotton + heating wire

The combination of cotton wick and heating wire is the most widely used atomization core form in electronic cigarettes. Even today, this technology is still widely used in many electronic cigarette products. Especially the introduction of “organic cotton” has improved the safety and taste of cotton core compared to fiberglass rope. In the era of DIY smog, cotton wicks have become almost the only choice for users.
Traditional cotton-core heating wire mainly uses cotton fiber as the oil-conducting material, and the heating wire is wrapped around it. The advantage of traditional cotton-core heating wire is that it has good oil absorption, oil storage and oil conductivity. However, the heating wire is wrapped around the cotton rope, which makes it difficult to control the consistency and is inconvenient to assemble. There are risks such as oil leakage and core smear.
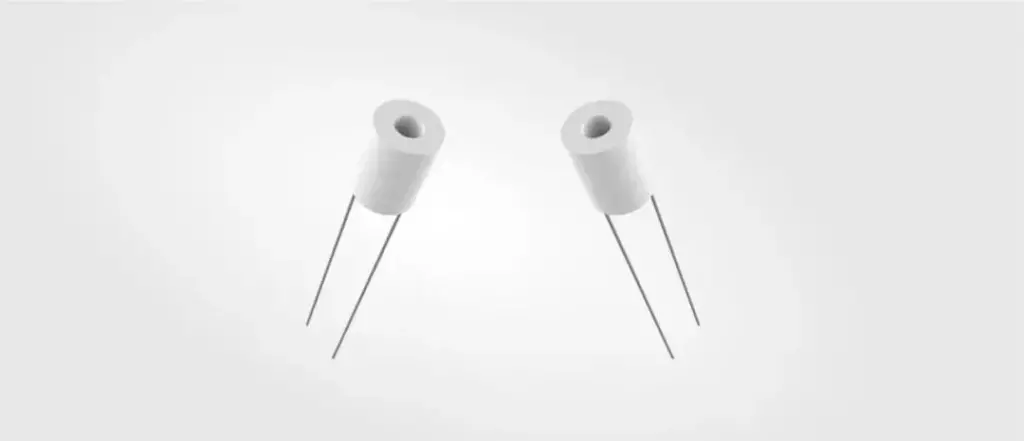
Third generation atomizing core: cylindrical ceramic core

With the development of electronic cigarettes, small cigarettes have gradually surpassed large cigarettes and become the mainstream of the market. In order to obtain a more stable atomization taste, manufacturers began to research on alternative materials for the atomization core, so microporous ceramic materials began to be applied.
Subsequently, the cylindrical ceramic atomizing core was born. The columnar ceramic heating wire is placed in the center hole of the ceramic. Compared with the cotton core, the taste is more stable and easier to assemble. But at the same time, the heating wire is easy to deform, has poor consistency, and occasionally has the risk of burning the core.
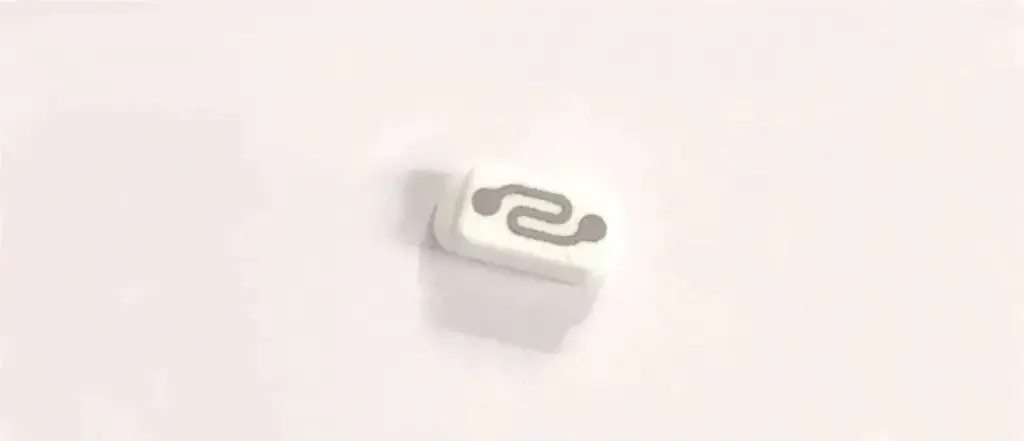
Fourth generation atomizing core: coated ceramic core

As the name suggests, the coated ceramic heating core is based on microporous ceramics and uses a metal slurry thick film printing process to “print” metal on the ceramic substrate. Compared with cylindrical ceramic cores, coated ceramic cores heat up faster and taste better.
The coated ceramic core is also one of the most widely used atomization technologies in POD reloadable e-cigarettes.
Fifth generation atomizer core: steel ceramic core

The steel sheet ceramic core is a new type of heating element made of microporous ceramic as the base, using inlay technology to embed metal mesh into the surface of the ceramic base. Because a whole piece of metal mesh is embedded into the surface of the ceramic base, it is strong and durable, more resistant to high temperatures, and not easy to break. Because the metal heats more uniformly, the heating area is larger, and the heating speed is faster, the smoke liquid is fully atomized instantly, resulting in a large amount of smoke, a purer and fuller taste, and a stronger throat hit.
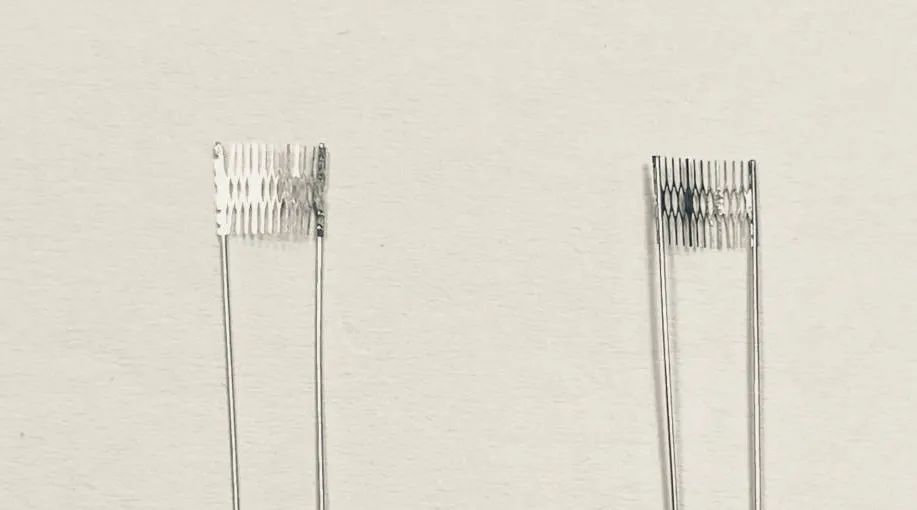
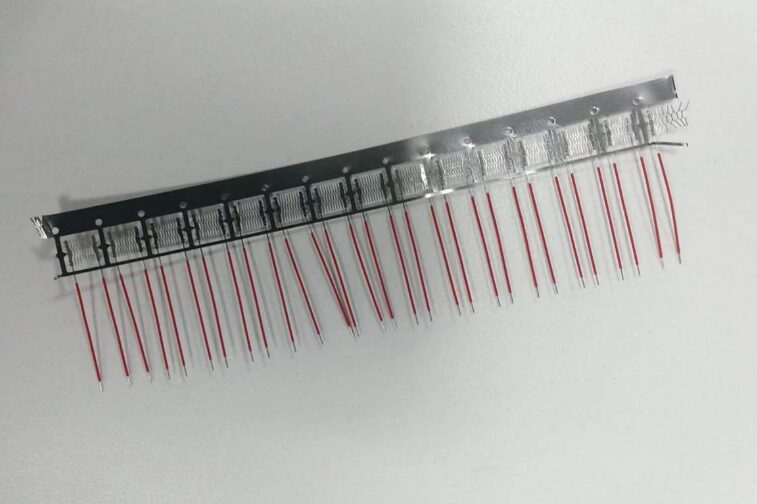
The sixth generation atomizer core: AX large smoke mesh core ceramic
AX large smoke mesh core ceramic adopts the sixth generation atomization technology in the atomization core industry. Adopting special technology and dual-mesh core heating, the heating area is increased by 2 times, and the heating start-up speed is 1.5 times faster. It truly achieves instant puffing and large smoke. The taste remains basically unchanged from the first to the last sip, giving consumers the ultimate experience. .
At the same time, the embedded heat is generated extremely quickly, the mist molecules are less than 0.6 microns, and the taste is very full, soft, and delicately fragrant. In addition, the 316 metal mesh core material, which is widely used in the food and medical fields, is used to ensure the safety of the material.
As for the preparation process of mesh core heating wire, there are currently three known methods: etching, stamping, and weaving.
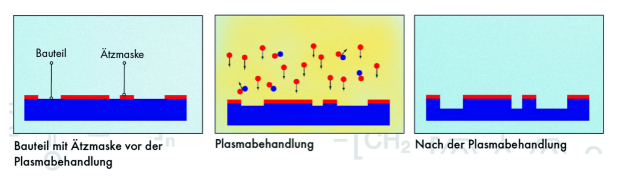
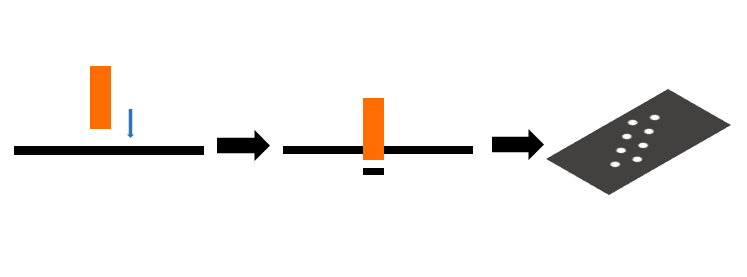
1. Etching: Also known as photochemical etching, it refers to removing the protective film from the area to be etched through exposure plate making and development, and then contacting the chemical solution during etching to achieve the effect of dissolving corrosion and forming concave and convex or hollow forming effects.
Process: cutting – cleaning – coating – exposure – development – etching – film replacement – film removal – inspection – packaging


2. Stamping: It is a forming processing method that relies on presses and molds to apply external force to plates, strips, pipes and profiles to cause plastic deformation or separation, thereby obtaining workpieces (stamping parts) of the required shape and size. It can Obtain shapes such as punching, bending, rounding, and drawing.
Process: Mold opening – punching – leveling – cutting – trimming – cleaning – post-processing (welding, bending, surface treatment, etc.)


Stamping mesh core heating wire
3. Weaving: As the name suggests, metal wires are woven into a mesh by crossing each other. According to industry insiders, the mesh core of IQOS VEEV is a woven mesh.
Process: wire drawing-braiding-cleaning-post-processing
Differences between mesh core heating wires prepared by three processes
It is understood that the main differences between the mesh core heating cores prepared by the three processes are as follows:
Etched sheets are currently the most widely used. The advantage is that the early proofing and delivery are faster, and the resistance value and circuit can be flexibly adjusted at any time. The disadvantage is that the cost is high and the resistance value error is easy to be too large;
Perforated mesh is currently used relatively rarely, but it is expected to become mainstream in the future, because punching has lower costs, higher precision, and faster production capacity ramp-up. However, the early mold opening cycle is relatively long, and the lines cannot be flexibly adjusted;
Woven mesh is currently rarely used in the industry, and there are few mature and stable suppliers. The atomization effect and heating uniformity of woven mesh like IQOS VEEV are the best.